
|
ROK |
MIESIAC |
DZIEN |
MIEJSCE |
TEMAT |
|
2003 |
Luty |
23 |
Bintan |
|
|
2003 |
Luty |
20-21 |
Bintan |
|
|
2003 |
Luty |
22 |
Bintan |
|
|
2003 |
Luty |
19 |
Bintan |
|
|
2003 |
Luty |
17-25 |
Bintan |
|
|
2003 |
Luty |
17-25 |
Bintan |
|
|
1992 |
Czerwiec |
|
Jawa, Bali |
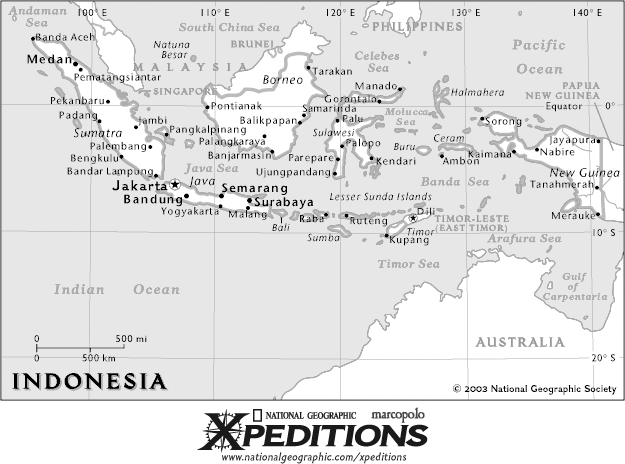
INDONEZJA,
Indonesia,
Republika Indonezji, Republik Indonesia,
państwo w pd.-wsch. Azji, na
Archipelagu Malajskim i w zach. części Nowej Gwinei,
między
O. Indyjskim i O. Spokojnym, po obu stronach równika;
rozciągłość z zach. na wsch. wynosi ponad 4800 km,
z pn. na pd. — 2000 km.
Informacje
ogólne
Stolica:
Dżakarta
Powierzchnia:
1919,4 tys. km2 (z wodami terytorialnymi 3772,2 tys. km2)
Ludność:
202,2 mln mieszk. (1997)
Język
urzędowy: bahasa indonesia (indonez.)
Jednostka
monetarna: rupia indonezyjska
Święto
narodowe: 17 sierpnia — dzień proklamacji
niepodległości (1945)
Podział
administracyjny: 27 prow., w tym 3 (Aceh, Dżakarta i Jogyakarta)
okręgi specjalne
Granica:
z Malezją (na Borneo) i Papuą-Nową Gwineą (na
Nowej Gwinei), cieśn. Malakka oddziela Indonezję od Malezji
i Singapuru, morza Sulu i Celebes — od Filipin, morza Timor
i Arafura — od Australii
Area
1,904,570 sq km (735,358 sq mi)
Population
220,483,000 (updated 2004)
Capital
Religions
Muslim, Protestant, Roman Catholic, Hindu, Buddhist
Languages
Bahasa Indonesia, English, Dutch, Javanese and other
local dialects
Literacy
84%
Life expectancy
68 years
GDP Per Capita
U.S. $3,000
Economy
Industry: petroleum and natural gas, textiles, mining, rubber.
Agriculture: rice, cassava, peanuts, rubber, poultry.
|
The
world's fourth most populous nation, Indonesia is the largest Islamic
country, with some 175 million Muslims. About 300 ethnic groups speak 365
local dialects on more than 13,660 islands. Unity and stability are
improving, although outer areas of the archipelago resent domination by Java. |
|
Text source: National
Geographic Atlas of the World, Seventh Edition, 1999 |